Demos: 1N-04 Conservation of Linear Momentum
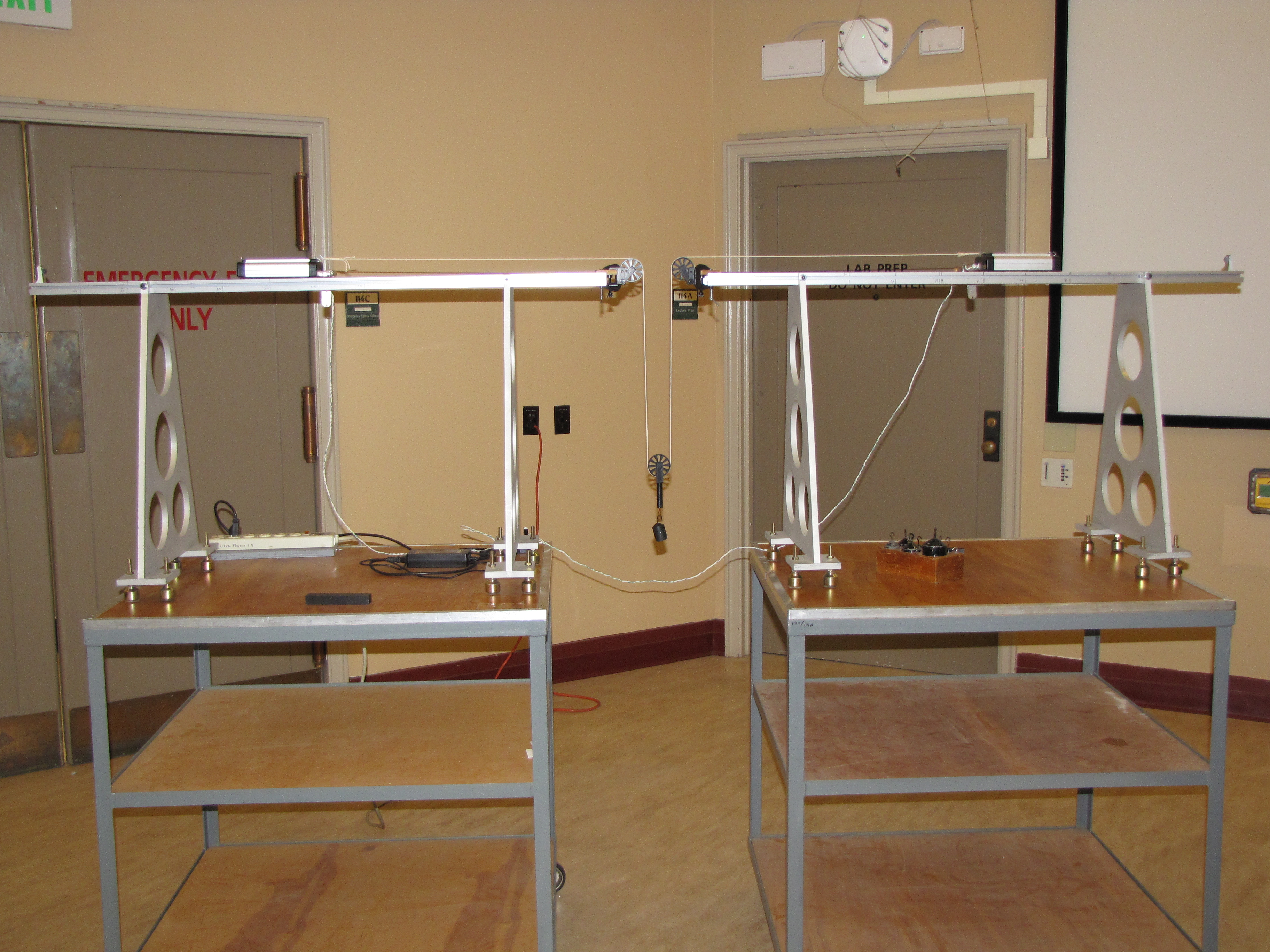

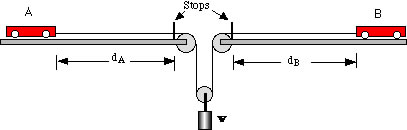
In this arrangement, a common force, w, imparts identical tensions to each of the strings connected to the carts. Thus the tensions are internal, equal and opposite forces and the momentum of the system is conserved. Since the carts start from rest (p = 0), we have at all times,
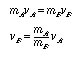
If Dt is the time for the cart to reach the stop, then
and
Combining these equations, we get
Then DtA = DtB if
Thus, if the masses are in inverse ratio to the initial distances, the carts will arrive at the stops simultaneously.
Directions: First make the cart masses and their respective distances equal. Allow the weight to fall and the carts will arrive at the stops at the same time. Then, say, double one mass and reduce the corresponding distance to one half its earlier value. Again the carts should reach the stops simultaneously.
Suggestions for Presentation: Establish the case for conservation of momentum before proceeding. Students should understand that the falling weight is imparting the same force to each cart and thus these forces comprise an internal action-reaction pair that cancel when considering the carts together as a system. Deciding whether to develop the full mathematical argument for showing the inverse ratio of masses and distances is an option if you are short on time, but some argument should be made for the plausibility of these results.
Applications: Various systems in which there are internal forces acting, resulting in no momentum change.
Last Updated: Nov 30, 2023 11:25 AM