 Hard hat Hard hat
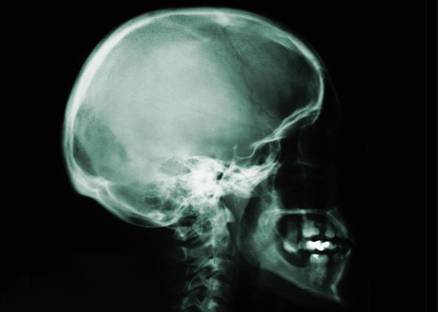
The skull effectively protects the brain up to a point.
Something falling on your head or walking into a hard object can cause a skull fracture, or more serious injuries.
Head protection is required for certain jobs because of the serious nature of head injuries.

 Head Protection (Hard hats) are required when working in an area where head injuries are likely.
The most common hazards requiring protection include falling or flying objects, or walking into or falling on hard objects.
For PRIME Lab, Hard hats are required when working with the crane where the load or hook is more than 4 feet above the floor.
A hard hat is also required when working in the accelerator tank with the floorboards removed.
A hard hat is not required for waling under foam protected sections of beam lines.
The requirements for use of these hard hats should be listed in the hazard assessment for the work area.
Head Protection (Hard hats) are required when working in an area where head injuries are likely.
The most common hazards requiring protection include falling or flying objects, or walking into or falling on hard objects.
For PRIME Lab, Hard hats are required when working with the crane where the load or hook is more than 4 feet above the floor.
A hard hat is also required when working in the accelerator tank with the floorboards removed.
A hard hat is not required for waling under foam protected sections of beam lines.
The requirements for use of these hard hats should be listed in the hazard assessment for the work area.

 Note that bump caps are not the same as impact hard hats, and cannot be used where a hard hat is required.
If the hard hat is to be used for electrical protection, it must be rated for that use by the manufacturer.
Hard hats have in inner suspension that must be made by the same manufacturer as the helmet and for the same model helmet.
The suspension must be installed according to the manufacturers instructions. It is necessary that
they fit well enough to not fall off, but not so tightly to be uncomfortable.
Note that bump caps are not the same as impact hard hats, and cannot be used where a hard hat is required.
If the hard hat is to be used for electrical protection, it must be rated for that use by the manufacturer.
Hard hats have in inner suspension that must be made by the same manufacturer as the helmet and for the same model helmet.
The suspension must be installed according to the manufacturers instructions. It is necessary that
they fit well enough to not fall off, but not so tightly to be uncomfortable.

 Carefully inspect the hat before donning (putting on).
Inspect the shell for any visible signs of dents, cracks, gouges, penetration, chalking, loss of gloss or any other signs of damage that might reduce the degree of safety originally provided. .
Inspect the suspension for cracked, torn or frayed straps. .
Once the inspection is complete, make sure that the hat is properly adjusted.
One type of suspension has a ratchet knob at the back of the suspension.
Put on the hat and tighten the suspension until it is snug, making sure that it doesn't fall off if you bend over.
The other common type of suspension has snaps in the back of the suspension, which you must adjust by trial and error.
When properly adjusted, it should sit comfortably, but securely on your head.
When removing (doffing) a hard hat, inspect it for damage and clean it if necessary.
Carefully inspect the hat before donning (putting on).
Inspect the shell for any visible signs of dents, cracks, gouges, penetration, chalking, loss of gloss or any other signs of damage that might reduce the degree of safety originally provided. .
Inspect the suspension for cracked, torn or frayed straps. .
Once the inspection is complete, make sure that the hat is properly adjusted.
One type of suspension has a ratchet knob at the back of the suspension.
Put on the hat and tighten the suspension until it is snug, making sure that it doesn't fall off if you bend over.
The other common type of suspension has snaps in the back of the suspension, which you must adjust by trial and error.
When properly adjusted, it should sit comfortably, but securely on your head.
When removing (doffing) a hard hat, inspect it for damage and clean it if necessary.
 Hard hats provide limited protection against falling objects.
They do not provide protection against very heavy falling objects, like a piano.
Do not walk under heavy objects supported by a crane.
They also do not provide protection against high velocity moving objects such as bullets. .
In order to be effective, the hat must be worn.
Hard hats provide limited protection against falling objects.
They do not provide protection against very heavy falling objects, like a piano.
Do not walk under heavy objects supported by a crane.
They also do not provide protection against high velocity moving objects such as bullets. .
In order to be effective, the hat must be worn.
 You can clean your hat with mild soap and hot water, rinse with clear water, wipe, and let†air dry.
Donít use paint, solvents, gasoline, chemicals, or harsh cleaning materials on the shell.
Donít put anything in the space between the suspension and the shell.
Because prolonged exposure to sunlight and heat can damage your hat, store it in†a clean, dry, and cool location out of direct sunlight.
Suspensions will deteriorate over time from exposure to sunlight and chemicals, perspiration and hair oils.
Replace hat when hairline cracks start to appear.
Replace hat that has been struck by a forceful object, even if no damage is obvious.
Replace the suspension when damage is noticed.
The suspensions typically have a useful life of one year if used daily.
The suspension may last longer, depending on usage.
The useful life of the shell will depend on the conditions of use and care.
Discard in regular trash when wear becomes obvious.
You can clean your hat with mild soap and hot water, rinse with clear water, wipe, and let†air dry.
Donít use paint, solvents, gasoline, chemicals, or harsh cleaning materials on the shell.
Donít put anything in the space between the suspension and the shell.
Because prolonged exposure to sunlight and heat can damage your hat, store it in†a clean, dry, and cool location out of direct sunlight.
Suspensions will deteriorate over time from exposure to sunlight and chemicals, perspiration and hair oils.
Replace hat when hairline cracks start to appear.
Replace hat that has been struck by a forceful object, even if no damage is obvious.
Replace the suspension when damage is noticed.
The suspensions typically have a useful life of one year if used daily.
The suspension may last longer, depending on usage.
The useful life of the shell will depend on the conditions of use and care.
Discard in regular trash when wear becomes obvious. |





 Hard hat
Hard hat

